Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronics Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, People’s Republic of China
2 Shandong Laboratory of Yantai Advanced Materials and Green Manufacturing, Yantai, 264006, People’s Republic of China
3 Key Laboratory of Material Physics, School of Physics and Microelectronics, Zhengzhou University, Ministry of Education, Zhengzhou 450052, People’s Republic of China
4 School of Electronics and Information Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, People’s Republic of China
5 Hoffmann Institute of Advanced Materials, Shenzhen Polytechnic, Shenzhen 518060, People’s Republic of China
Single materials that exhibit efficient and stable white-light emission are highly desirable for lighting applications. This paper reports a novel zero-dimensional perovskite, Rb4CdCl6:Sn2+, Mn2+, which demonstrates exceptional white-light properties including adjustable correlated color temperature, high color rendering index of up to 85, and near-unity photoluminescence quantum yield of 99%. Using a co-doping strategy involving Sn2+ and Mn2+, cyan-orange dual-band emission with complementary spectral ranges is activated by the self-trapped excitons and d-d transitions of the Sn2+ and Mn2+ centers in the Rb4CdCl6 host, respectively. Intriguingly, although Mn2+ ions doped in Rb4CdCl6 are difficult to excite, efficient Mn2+ emission can be realized through an ultra-high-efficient energy transfer between Sn2+ and Mn2+ via the formation of adjacent exchange-coupled Sn–Mn pairs. Benefiting from this efficient Dexter energy transfer process, the dual emission shares the same optimal excitation wavelengths of the Sn2+ centers and suppresses the non-radiative vibration relaxation significantly. Moreover, the relative intensities of the dual-emission components can be modulated flexibly by adjusting the fraction of the Sn2+ ions to the Sn–Mn pairs. This co-doping approach involving short-range energy transfer represents a promising avenue for achieving high-quality white light within a single material.
Nano-Micro Letters
2023, 15(1): 207

Author Affiliations
Abstract
International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronics Science and Technology of Ministry of Education, Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
In this paper, a controllable one-step doping method has been successfully adopted in the cesium copper iodide perovskite’s luminescence, a high-quality white-light emission with Commission Internationale de l′Eclairage (CIE) coordinates of (0.3397, 0.3325), and a color rendering index (CRI) reaching up to 90 was realized in a convenient way. Through adding impurities into the system, high efficiency and stable was synthesized, and the coexistence of varied high luminescence phases realized the white lighting. Strikingly, blue-emitting and yellow-emitting could coexist, and their respective luminescence was not interacted in the compound, which was beneficial for acquiring a single emission and highly efficient white lighting. This work carried out a deep exploration of the Cu-based metal halides, and would be favorable to the applications of lead-free perovskites.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(5): 05000694
Author Affiliations
Abstract
International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronic Science & Technology of Ministry of Education, Engineering Technology Research Center for 2D Material Information Function Devices and Systems of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen518060, China
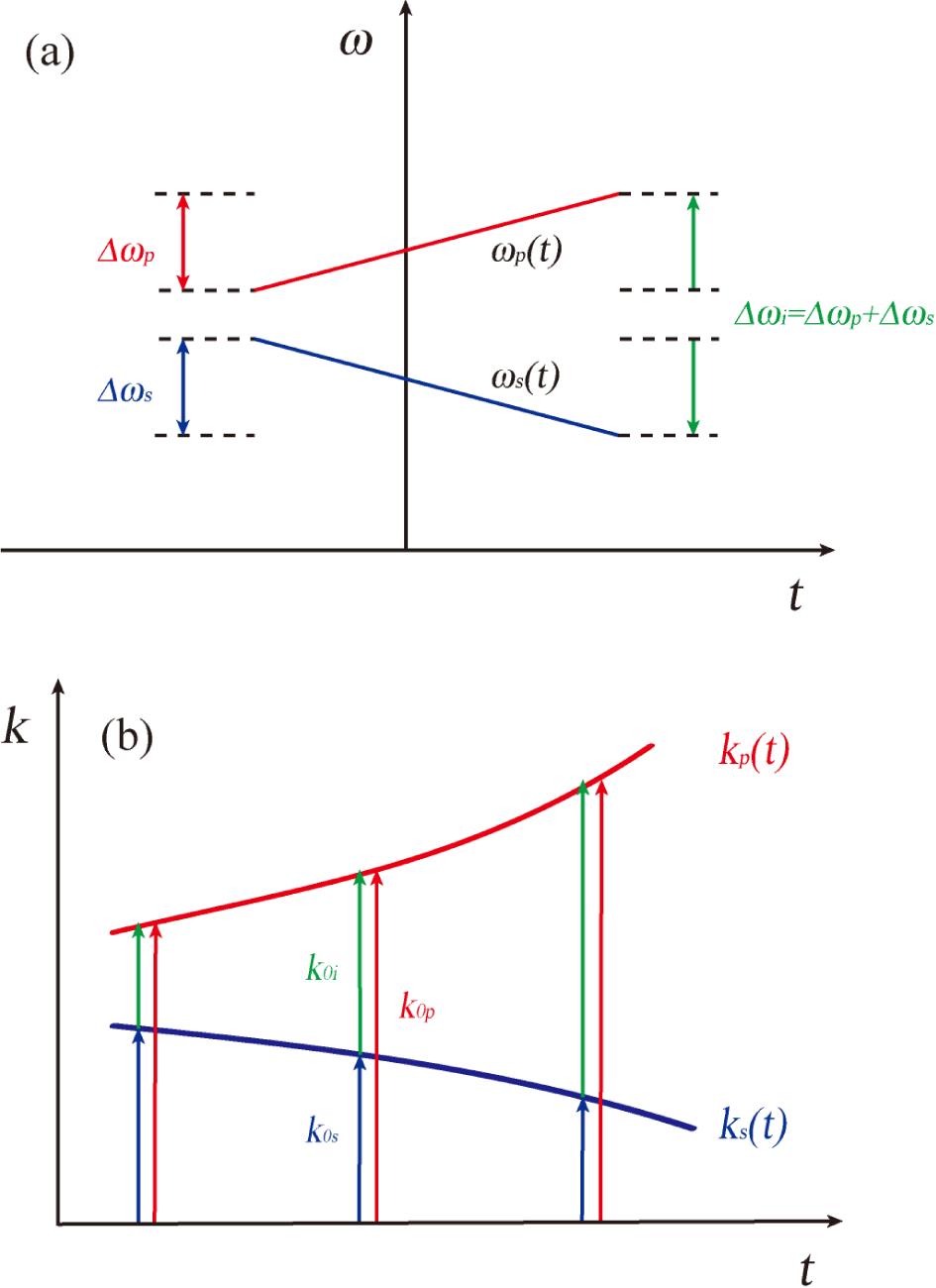
Dual-chirped difference frequency generation (DFG) is an advantageous technique for generating the broadband mid-infrared (IR) idler wave, which is inaccessible by a population-inversion-based laser system. In principle, the generated idler wave may even suffer a spectrum broadening compared with the driving pulsed lasers if the pump and signal waves are oppositely chirped. However, broadband phase-matching is always the determining factor for the resulting efficiency and the bandwidth of the generated idler wave. In this study, specific to an oppositely dual-chirped DFG scheme, we derive the precondition to realize broadband frequency conversion, wherein a negative $(1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{p}-1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{i})/(1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{s}-1/\unicode[STIX]{x1D710}_{i})$, in terms of the correlation coefficient of the group velocity ($\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$), is necessary. However, most birefringence bulk crystals can only provide the required material dispersions in limited spectral regions. We show that the periodically poled lithium niobate crystal that satisfies an inactive Type-II (eo-o) quasi-phase-matching condition has a stable negative $\unicode[STIX]{x1D70E}$ and exerts the expected broadband gain characteristic across an ultra-broad idler spectral region $(1.7{-}4.0~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m})$. Finally, we propose and numerically verify a promising DFG configuration to construct a tunable mid-IR spectrum broader based on the broadband phase-matched oppositely dual-chirped DFG scheme.
mid-infrared optical parametric amplification periodically poled lithium niobate crystal ultrafast laser High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2020, 8(2): 02000e27
Author Affiliations
Abstract
International Collaborative Laboratory of 2D Materials for Optoelectronic Science & Technology of Ministry of Education, Engineering Technology Research Center for 2D Material Information Function Devices and Systems of Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
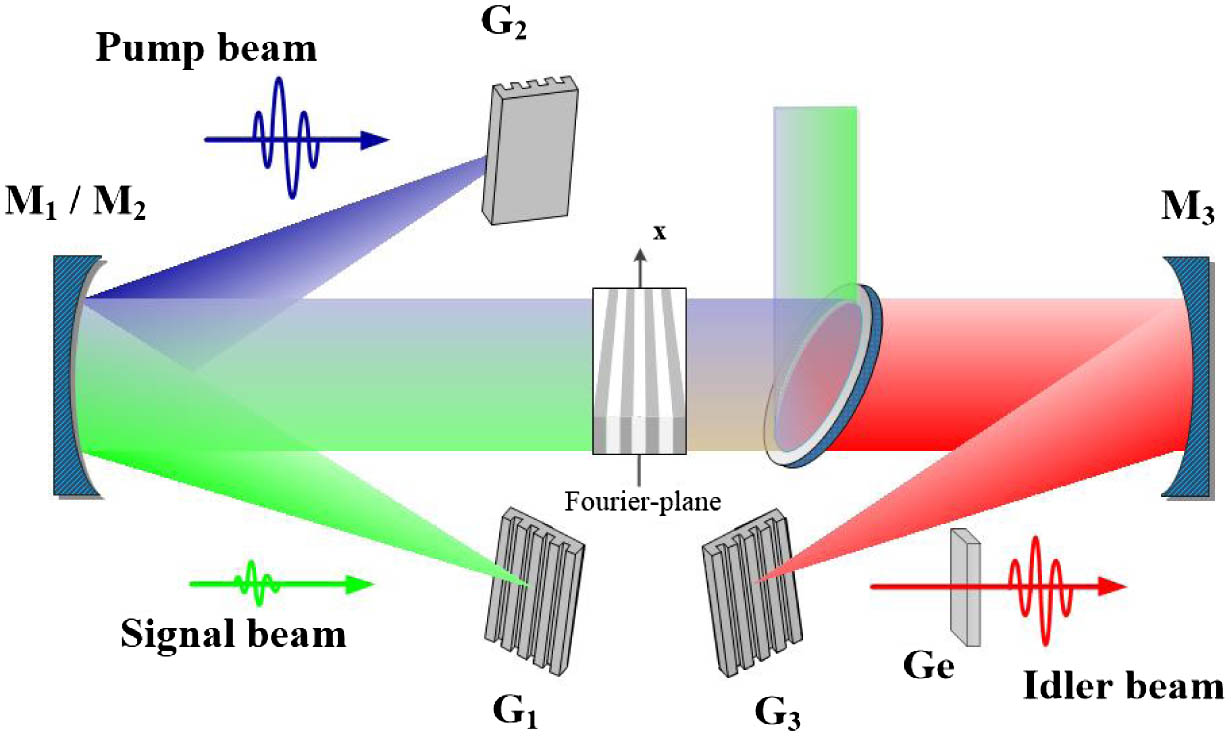
An opposite-chirped frequency-domain optical parametric amplification (OC-FOPA) design is demonstrated and numerically verified. This scheme combines both an ultrabroad seeding generation and the subsequent effective amplification in one single optical parametric amplification stage. Based on a slightly asymmetrical 4-f optical system, the spectral contents of both pump and signal waves are spectrally dispersed with opposite spatial chirps, to broaden the initial idler seeding. Via a properly designed fan-out periodically poled LiNbO3 chip, nearly perfect quasi phase matching can be realized across the full spectrum, whereby each individual spectral pair precisely maps to its required grating period. Full-dimensional simulations based on commercial ~110 fs (FWHM) near-infrared (near-IR) lasers at 790 and 1030 nm are quantitatively discussed, and few-cycle mid-IR laser pulses (~60 fs at 3.4 μm) plus a high conversion efficiency exceeding 50% are theoretically predicted. By means of a high-power pump source, the OC-FOPA scheme can be also applied to directly produce high-intensity carrier-envelope-phase-stabilized mid-IR idler pulses.
(190.4970) Parametric oscillators and amplifiers (320.7110) Ultrafast nonlinear optics (320.7160) Ultrafast technology. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000669
1 深圳大学光电工程学院光电子器件与系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
2 长沙学院电子与通信工程系, 湖南 长沙 410003
3 湖南第一师范学院信息技术系, 湖南 长沙 410205
4 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
实验研究了圆孔衍射调制下的强激光在克尔非线性介质中的传输特性。观测了小尺度自聚焦效应引起的多细丝形成、单根细丝演化以及细丝之间相互作用过程。结果表明: 在非线性传输过程中,衍射调制光束在空间特定位置出现调制增长,导致光束分裂形成多路细丝;单根细丝的强度并非无限增长,而是达到一定值后通过锥形发射释放多余能量,同时与背景光相互作用形成新细丝;相距较近的细丝之间通过干涉相互作用,使其在附近区域形成新的细丝。
非线性光学 自聚焦 非线性传输 小尺度自聚焦 衍射 中国激光
2014, 41(12): 1202008





